Discover everything about Bitcoin Ordinals, including their marketplace, wallet, price, and NFTs. Learn how Bitcoin Ordinals are reshaping the market cap and what makes them unique.
Table of Contents
✅ Part 1: Introduction
🔹 What are Bitcoin Ordinals?
Bitcoin Ordinals are a groundbreaking innovation that allows individual satoshis (the smallest units of Bitcoin) to carry unique, embedded data—such as text, images, or other files—directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. This process is known as “inscription”, and it effectively transforms satoshis into non-fungible digital artifacts, comparable to NFTs, but with some fundamental differences in structure and storage.
The Ordinals Protocol, introduced by software engineer Casey Rodarmor in early 2023, takes advantage of Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade, enabling arbitrary data to be added to individual satoshis without altering the base layer of the blockchain. This capability expands Bitcoin’s utility far beyond peer-to-peer payments.
🔹 Why They’re Being Called the “NFTs of Bitcoin”
Bitcoin Ordinals have earned the nickname “NFTs of Bitcoin” because they mirror the functionality of NFTs on Ethereum and other chains—unique, verifiable, digital ownership of content—but with crucial distinctions:
- On-chain storage: Unlike many NFTs which merely point to metadata stored off-chain (e.g., on IPFS), Ordinals inscribe the actual data on the blockchain.
- No smart contracts needed: Ordinals operate purely on Bitcoin’s existing infrastructure, making them trustless and permissionless.
- Stronger permanence: Once inscribed, the data is immutable and stored forever in Bitcoin blocks.
This evolution has effectively given Bitcoin its own version of a decentralized content layer, making it possible to create digital collectibles, documents, artworks, and more—without leaving the Bitcoin ecosystem.

✅ Part 2: How Bitcoin Ordinals Work
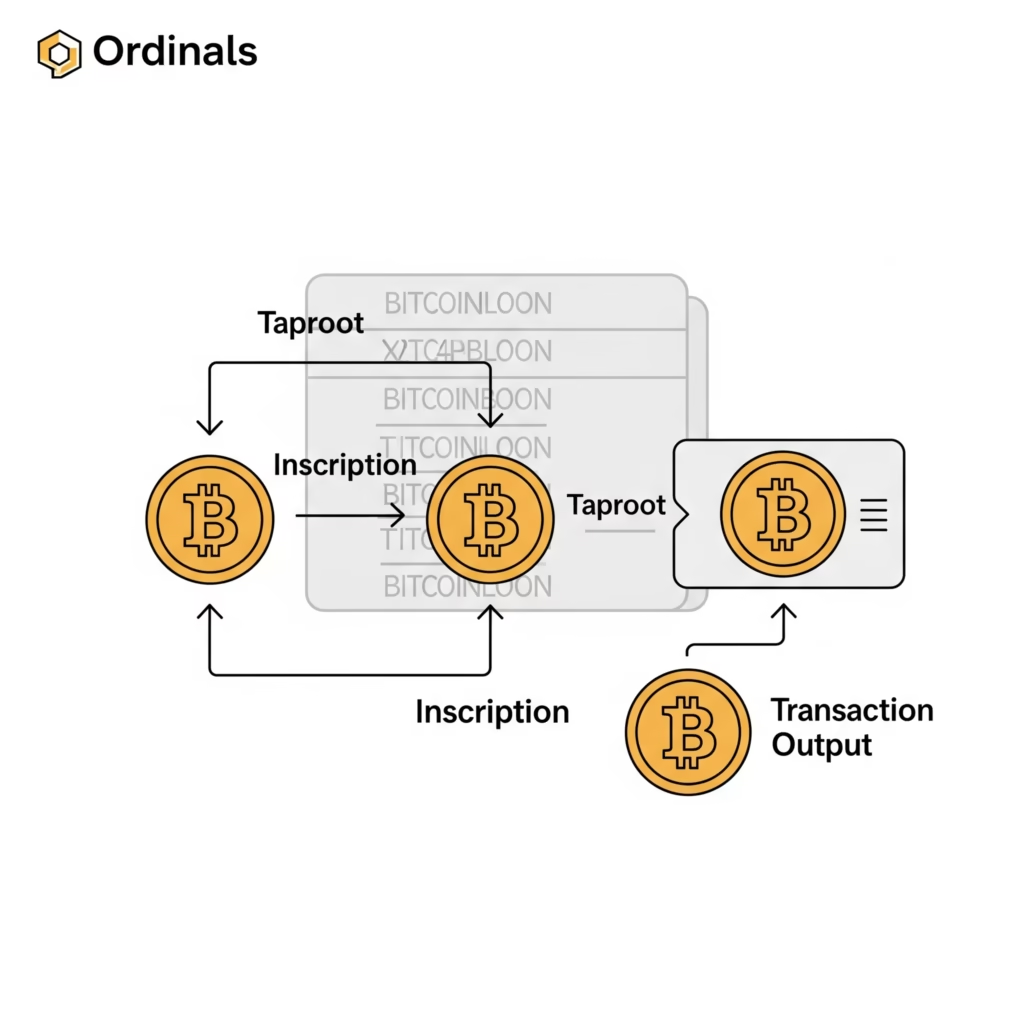
Bitcoin Ordinals function by embedding data directly onto individual satoshis—the smallest divisible units of a Bitcoin (1 BTC = 100,000,000 sats)—using a method called inscription. Here’s a breakdown of how it all works:
🔹 Inscriptions on Individual Satoshis
Each satoshi is treated like a blank canvas. Through the Ordinal Theory, every satoshi is assigned a serial number based on its order of mining and transaction history. These serial numbers make each satoshi individually traceable.
- A user can inscribe data—such as an image, text, or code—onto a satoshi using a specialized Bitcoin transaction.
- This inscription is stored on-chain, directly within the Bitcoin blockchain via the witness data structure introduced in SegWit and Taproot upgrades.
- This turns that satoshi into a digital artifact, permanently linked with its unique content.
Example:
A .PNG image of 150KB could be inscribed onto a single satoshi and become a Bitcoin-native NFT.
🔹 Use of the Ordinals Protocol
The Ordinals protocol is the system that tracks and indexes these inscribed satoshis.
- Built by Casey Rodarmor, it doesn’t change Bitcoin’s base layer.
- Instead, it uses existing structures like Taproot scripts to insert arbitrary data into transactions.
- It also uses a set of rules to keep track of which satoshis are inscribed and where they reside.
This protocol essentially overlays a naming and content-addressing system on top of the raw Bitcoin transaction layer.
🔹 Key Difference from Ethereum NFTs
While Ethereum NFTs (like those based on the ERC-721 or ERC-1155 standards) have dominated the non-fungible space, Bitcoin Ordinals offer a distinct approach:
| Feature | Bitcoin Ordinals | Ethereum NFTs |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Fully on-chain (data stored in Bitcoin) | Mostly off-chain (e.g., IPFS links) |
| Smart Contracts | Not required | Core component |
| Minting Process | Via inscription in Taproot transactions | Via contract interaction |
| Immutability | True on-chain permanence | Depends on smart contract implementation |
| Security Model | Bitcoin’s base-layer security | Ethereum base-layer + smart contract logic |
Bitcoin Ordinals represent a radical, minimalistic, and secure form of digital ownership by repurposing Bitcoin’s robust infrastructure. Unlike Ethereum’s NFT model, Ordinals achieve permanence without the need for extra layers or reliance on external file systems.
✅ Part 3: Technological Innovation Behind Ordinals
Bitcoin Ordinals are more than just a digital collectible trend — they represent a significant technological evolution in how data is handled on the Bitcoin network. Unlike Ethereum NFTs, which rely on smart contracts and external storage, Ordinals are powered by native Bitcoin upgrades that allow complete on-chain inscription.
⚙️ Taproot: The Catalyst for Ordinals
The Taproot upgrade, activated on the Bitcoin network in November 2021, is the cornerstone technology behind Bitcoin Ordinals. It introduced:
- Enhanced scripting capabilities via the Tapscript language.
- Improved privacy by making complex transactions appear like simple ones.
- Smaller transaction sizes, which make data embedding more feasible.
Without Taproot, the Ordinals protocol wouldn’t exist in its current form.
📦 Native BTC Data Embedding
Before Taproot, embedding arbitrary data into Bitcoin transactions was inefficient and expensive. Now, Taproot enables:
- Data inscription directly onto individual satoshis (the smallest BTC unit).
- This makes each satoshi traceable, transferable, and non-fungible, much like how ERC-721 tokens work on Ethereum.
This on-chain inscription model ensures full immutability and permanence, setting Bitcoin Ordinals apart from typical NFTs stored on IPFS or centralized servers.
🚫 No Smart Contracts Required
Ethereum NFTs require complex smart contracts to mint, transfer, and validate ownership. Bitcoin Ordinals don’t need smart contracts at all. The metadata and media are directly embedded into the satoshi using:
- Ordinal Theory, which serializes each satoshi.
- A custom indexing system to keep track of satoshi inscriptions.
This results in:
- Higher security (no contract bugs).
- Lower complexity and maintenance.
- Better decentralization, as the Bitcoin network doesn’t rely on external logic layers.
📊 Summary Table
Here’s a quick summary of the technological innovations:
| Component | Description | Impact on Ordinals |
|---|---|---|
| Taproot | Bitcoin upgrade enabling advanced scripts and data handling | Allows efficient on-chain inscription of digital artifacts |
| Data Embedding | Embedding media and metadata directly into satoshis | Provides full immutability without external links |
| No Smart Contracts | Uses Bitcoin’s UTXO model and Ordinal protocol | Eliminates security risks and contract complexity |

✅ Part 4: Ordinals vs Ethereum NFTs — A Comparative Breakdown
Bitcoin Ordinals and Ethereum NFTs may serve similar functions — owning, displaying, and trading digital assets — but they differ fundamentally in architecture, cost, and permanence. Here’s a breakdown of how these two systems stack up.
🛡️ Decentralization
- Bitcoin Ordinals are inscribed directly into the Bitcoin blockchain on individual satoshis.
- ✅ Truly immutable: The data is stored on-chain forever, not relying on external servers or smart contracts.
- ✅ No need for third-party platforms or marketplaces to validate ownership or media.
- Ethereum NFTs, on the other hand, often rely on smart contracts and store media off-chain via:
- ❌ IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
- ❌ Centralized hosting like AWS/CDNs
- ✅ Metadata and ownership tracked via ERC-721 or ERC-1155 smart contracts.
Verdict: Ordinals offer deeper decentralization as both metadata and content are on-chain.
💰 Cost Efficiency
- Ordinals:
- Minting an Ordinal requires a Bitcoin transaction with a Taproot script.
- Costs are influenced by the file size and current BTC gas (fee) rates.
- ⚠️ Larger inscriptions (e.g., HD videos or complex images) can be expensive.
- Ethereum NFTs:
- Smart contract deployments and minting on Ethereum can be very costly, especially during peak usage.
- Ethereum gas fees can spike drastically based on network congestion.
Verdict: Ordinals may be cheaper for small media inscriptions, but less scalable for large files. Ethereum NFTs are more predictable but costly due to smart contract execution.
🧠 Storage Permanence
- Bitcoin Ordinals:
- Permanently embedded on-chain — nothing can be deleted or changed.
- ✅ Guaranteed permanence and verifiability for as long as Bitcoin exists.
- Ethereum NFTs:
- Media is often stored externally, either on IPFS (decentralized) or centralized servers.
- Metadata may become inaccessible if the hosting service fails or is shut down.
Verdict: Ordinals win in long-term storage reliability due to full on-chain architecture.
📊 HTML Comparison Table
| Feature | Bitcoin Ordinals | Ethereum NFTs |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Fully on-chain; no smart contracts or external links required | Smart contracts for metadata; media often stored off-chain |
| Cost | Low for small files; cost scales with size and network fees | Gas fees vary; smart contract deployment adds cost |
| Storage Permanence | Permanent on-chain inscription | Depends on external hosting (IPFS or centralized) |
✅ Part 5: Use Cases of Bitcoin Ordinals
The Bitcoin Ordinals protocol is rapidly gaining traction beyond just the NFT scene. Its ability to inscribe immutable data directly onto individual satoshis (the smallest units of BTC) opens up powerful, censorship-resistant use cases across industries.
🎨 1. Art & Digital Collectibles (Bitcoin-native NFTs)
Bitcoin Ordinals have redefined NFTs by enabling true on-chain art.
- Artists can now inscribe entire artworks directly onto satoshis — ensuring:
- 🛡️ Permanence (art cannot be deleted or censored)
- 🔍 Provenance (ownership is traceable on Bitcoin’s immutable ledger)
- 🌐 Global accessibility (no reliance on centralized platforms like OpenSea)
Popular collections:
- Ordinal Punks – A spin on CryptoPunks, but fully stored on Bitcoin
- Taproot Wizards – Hand-drawn wizard art showcasing Taproot’s power
🗃️ 2. Immutable Records
The inscription mechanism can be used to store tamper-proof records, such as:
- 📜 Legal contracts and agreements
- 🧬 Genetic or health data (encrypted)
- 📈 Audit trails and timestamped logs
Why it’s powerful:
- ✅ Resists censorship and fraud
- ✅ Accessible globally without the need for trusted intermediaries
- ✅ Leverages Bitcoin’s robust security model
📰 3. Decentralized Publishing & Messaging
Ordinals can also support the decentralized distribution of content such as:
- Blog posts
- Journals
- Encrypted messages
- Whistleblower disclosures
This use case is critical in regions where:
- 🛑 Freedom of speech is limited
- 🌐 Internet censorship is high
- 🎯 Publishing needs anonymity and permanence
Example: Entire books or essays are being inscribed one page per Ordinal, creating a permanent, uncensorable archive.
📊 Table: Use Cases of Bitcoin Ordinals
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Art & NFTs | Artwork inscribed directly onto satoshis, similar to NFTs | True on-chain storage, provenance, no smart contracts needed |
| Immutable Records | Store legal docs, logs, and other critical data on Bitcoin | Tamper-proof, globally accessible, long-term reliability |
| Decentralized Publishing | Distribute written content directly through inscriptions | Censorship resistance, anonymity, guaranteed accessibility |
✅ Part 6: Benefits and Challenges of Bitcoin Ordinals
Bitcoin Ordinals bring an innovative twist to Bitcoin’s capabilities — enabling NFTs and data storage without smart contracts. But like any emerging technology, they come with both transformational advantages and critical trade-offs.
✅ Benefits of Bitcoin Ordinals
1. Immutable Data Storage
- Once inscribed, the data becomes permanent and unchangeable, as it’s embedded directly in the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Ideal for storing artwork, records, or any content requiring long-term preservation.
2. Trustless and Censorship-Resistant
- No reliance on third-party platforms.
- Resistant to takedowns or content censorship (crucial in oppressive regimes).
3. Decentralized by Nature
- Bitcoin Ordinals leverage the world’s most secure and decentralized blockchain.
- Inscriptions are accessible from any full Bitcoin node — no servers or APIs needed.
4. No Smart Contract Dependencies
- Unlike Ethereum NFTs, Ordinals don’t require complex contract deployment.
- This reduces the risk of smart contract bugs or exploits.
⚠️ Challenges of Bitcoin Ordinals
1. Block Space Congestion
- Inscriptions take up space in Bitcoin blocks.
- Large-scale usage of Ordinals can lead to higher transaction fees and network congestion, as seen during BRC-20 hype.
2. Ecosystem Still Maturing
- Tooling, wallets, and marketplaces are still under development.
- Compared to Ethereum, users face more friction in interacting with Ordinals today.
3. Community Controversy
- Bitcoin purists argue Ordinals clutter the blockchain, which should primarily be for monetary transactions.
- Others see it as a necessary evolution for Bitcoin utility.
📊 Table: Pros and Cons of Bitcoin Ordinals
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Immutable and permanent; native to Bitcoin | Consumes limited block space, increasing fees |
| Decentralization | No central servers; fully trustless access | Requires full node for optimal interaction |
| Security | Protected by Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work consensus | Still new, tooling not fully matured |
| Adoption | New use cases like NFTs and digital archives | Community split on impact and legitimacy |
✅ Part 7: Market Growth and Trends in 2025
As Bitcoin Ordinals move from experimentation to adoption, 2025 is shaping up to be a breakout year. A growing number of creators, collectors, and investors are recognizing Ordinals as a legitimate digital asset class—not just a novelty.
📈 Ordinals Adoption: Stats & Growth Trends
- Total inscriptions surpassed 60 million by Q1 2025 (up from ~50M in late 2024).
- Over $500 million in cumulative Ordinals transaction volume.
- Top collections like Bitcoin Punks, Ordinal Maxi Biz, and NodeMonkes are consistently trending in secondary markets.
💡 Table: Ordinals Adoption Milestones
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 (Q1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Inscriptions | 500,000+ | 50 million+ | 60 million+ |
| Ordinal Transaction Volume | $30M+ | $250M+ | $500M+ |
| Active Marketplaces | 3–5 | 10+ | 20+ |
🛒 Major Platforms and Marketplaces
In 2025, the Ordinals ecosystem has matured with robust infrastructure:
- Magic Eden (Bitcoin) – Now one of the top Ordinals marketplaces, offering creator tools, auction features, and verified collections.
- Gamma.io – Focused on creators and digital artists; seamless inscription minting.
- Unisat – Known for supporting both BRC-20 tokens and NFT-style Ordinals.
- Ordx.io – Lightweight marketplace for trading inscriptions directly via wallets.
💼 Investor & Creator Outlook
📊 Investor Sentiment
- Institutional funds and crypto VCs are actively entering the space, seeing Bitcoin NFTs as more secure and long-lasting than Ethereum counterparts.
- Collectors value permanence — no risk of metadata loss, making Bitcoin NFTs ideal for high-value digital art.
🎨 Creator Insights
- Artists are exploring Ordinals for exclusive drops, immutable publishing, and even music albums.
- Platforms like Gamma and Magic Eden are rolling out creator rewards, royalties, and launchpad support.
🚀 Key Takeaway
Bitcoin Ordinals have moved beyond experimentation. With surging adoption, maturing tools, and a growing creator economy, they represent a powerful trend reshaping how value and creativity intersect on the blockchain in 2025.
✅ Part 8: Wallets and Tools for Ordinals in 2025
🔐 Best Wallets for Bitcoin Ordinals (2025)
In 2025, several wallets now natively support Ordinals and BRC-20 tokens, making inscriptions, storage, and transfers more user-friendly.
✅ Top Wallets Supporting Bitcoin Ordinals
| Wallet | Features | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Unisat Wallet | Supports BRC-20, Ordinals, inscription creation, token minting | Chrome extension |
| Xverse Wallet | Ordinals support, Taproot address compatibility, NFT viewer | Mobile (iOS/Android), Browser extension |
| Hiro Wallet | Stacks-based, supports Bitcoin NFTs, secure Taproot keys | Browser and desktop |
| Leather Wallet (formerly Sparrow fork) | Supports PSBT signing for Ordinal transactions | Desktop |
🛠️ Inscription Tools & Marketplaces
Most marketplaces now offer no-code tools for minting inscriptions directly.
- Gamma.io – Drag-and-drop interface for artists.
- Unisat.io – Allows both BRC-20 and NFT-style Ordinal minting.
- OrdinalsBot – Automates inscription process for bulk uploads.
👨💻 Developer Toolkits & SDKs
For developers looking to build on Ordinals or integrate inscription features:
| Tool | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ord (CLI) | Official Ordinals protocol implementation in Rust | Create/view inscriptions, run nodes |
| OpenOrd SDK | Open-source SDK to interact with inscriptions | Wallet and marketplace integrations |
| Ordinals Indexer APIs | APIs to fetch inscription data, ownership, and markets | Explorer and marketplace development |
📌 Summary
Bitcoin Ordinals are now backed by a fully functioning tech stack:
- User-facing wallets for both desktop and mobile
- Drag-and-drop inscription tools
- Developer SDKs to extend marketplace and app functionality
✅ Part 9: Regulatory Landscape for Bitcoin Ordinals
⚖️ Legal Recognition of Bitcoin Ordinals
As of 2025, Bitcoin Ordinals operate in a gray legal zone globally. Since inscriptions can include images, videos, documents, or code directly on-chain, regulators have begun assessing their implications under intellectual property, cybercrime, and financial securities laws.
Key Points:
- USA: SEC hasn’t classified Ordinals as securities, but concerns exist if used in fundraising.
- EU: GDPR implications for immutable personal data on-chain.
- Asia: Japan and South Korea have issued guidance on NFT compliance, but not yet on Ordinals.
⚠️ Data Permanence & Legal Risks
One of the core features of Ordinals—immutability—is also a source of legal scrutiny.
🚨 Risks:
- Illegal or harmful content can be inscribed permanently, making it impossible to remove or censor.
- No central authority can moderate or delete these inscriptions.
- Hosting nodes may unknowingly distribute illegal content embedded in the blockchain.
🔐 Developer Response:
| Issue | Mitigation Attempt | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Inscriptions with prohibited content | Blacklist support added to explorers and wallets | Medium – only affects UI, not blockchain |
| Content moderation | Manual flagging on marketplaces like Gamma, Unisat | Low – still accessible via raw blockchain |
| GDPR conflict (right to be forgotten) | Limited by the nature of blockchain; no clear fix | Unresolved |
🌍 Jurisdictional Challenges
| Region | Regulation Status | Key Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Unclear | May regulate if used for fundraising (SEC) |
| EU | Under GDPR scrutiny | Data immutability vs privacy |
| India | No specific regulation | Under crypto monitoring framework |
| China | Banned | All crypto and NFT activity restricted |
| Japan | NFT-friendly | Ordinals not yet regulated |

📝 Summary
The regulatory future of Bitcoin Ordinals hinges on:
- Whether inscriptions will be seen as speech, code, or security.
- Global consensus on how to treat immutable data.
- Development of standards for content moderation and responsibility.
✅ Part 10: Future Outlook & Final Thoughts
📈 Bitcoin Ordinals: Future Outlook for 2025 and Beyond
As we step into the mid-2020s, Bitcoin Ordinals stand at the intersection of innovation and decentralization. This disruptive approach—embedding data directly onto Bitcoin’s base layer—signals a radical shift in how digital assets can exist and persist.
🔮 What’s Ahead?
- Increased Developer Tooling: As the Ordinals protocol matures, developers are building wallets, explorers, and minting tools tailored to this ecosystem. Expect better user interfaces and more dev-friendly SDKs by the end of 2025.
- Broader Institutional Awareness: Institutional players like asset managers and exchanges are beginning to take note of Ordinals’ permanence. Several pilot programs for archival and ownership record-keeping on BTC are already under consideration.
- Layer 2 Integration: Lightning Network and other Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions may soon integrate Ordinals capabilities for scalability, reducing block space bloat concerns.
- Compliance Solutions: Privacy-focused features such as Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) may be layered on top to address regulatory concerns like GDPR compliance and financial KYC/AML requirements.
✅ Final Thoughts
Bitcoin Ordinals are not just another crypto novelty—they’re potentially a foundational layer for Bitcoin-native applications. Unlike Ethereum NFTs, which rely on smart contracts and external metadata, Ordinals embrace Bitcoin’s immutable, minimalist ethos. In doing so, they represent a new era for Bitcoin’s programmability and cultural relevance.
With growing adoption, deeper tooling, and increasing attention from creators and investors alike, Bitcoin Ordinals could redefine what permanence, value, and expression mean in the digital world.

Low Market Cap Crypto with Huge Potential
know more about Bitcoin Ordinals



